Интересное сегодня
Моральный гнев и его влияние на онлайн-активизм: что работае...
Введение Исследование, проведенное командой ученых под руководством доктора Стефана Лича из Ланкасте...
Роль знакомости последовательностей в проверке порядка
Введение Обработка порядка считается важным аспектом числового развития. Например, чем быстрее челов...
Диагностика СДВГ у собак: новый метод на основе человеческих...
Введение Синдром дефицита внимания и гиперактивности (СДВГ) — одно из самых распространённых нейрора...
Как маскировка аутизма влияет на мозг подростков: новое иссл...
Как маскировка аутизма влияет на мозг подростков Некоторые подростки с аутизмом скрывают свои особен...
Влияние родительской тревоги на психическое здоровье ребенка...
Введение Многочисленные исследования демонстрируют широкое влияние общей родительской тревожности на...
Влияние ранних жизненных трудностей на развитие и привязанно...
Новое исследование демонстрирует, что даже незначительные ранние жизненные трудности могут нарушить ...
Introduction
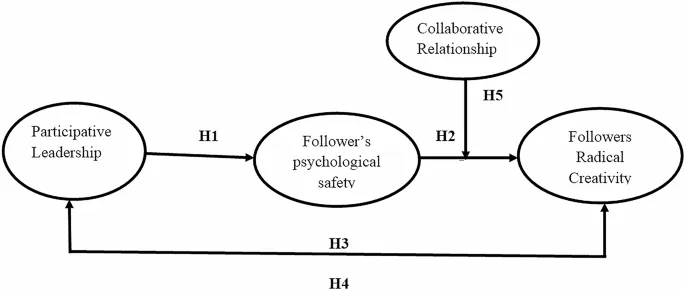
Creativity and innovation are essential for organizations to survive and thrive in today's fast-paced and competitive environment. Leaders play a crucial role in fostering follower radical creativity (FRC) and promoting entrepreneurial innovation. This study aims to understand how participative leadership (PL) affects followers' psychological safety (FPS) and enhances their FRC through collaborative relationships.
The Role of Participative Leadership
Participative leadership involves engaging followers in decision-making processes, creating a psychologically safe environment where they feel secure and empowered to take risks and share knowledge. This leadership style encourages intrinsic motivation, facilitates problem-solving, and promotes a positive team climate.
Follower Radical Creativity
Follower radical creativity refers to the generation of innovative and valuable concepts that deviate from conventional approaches. It is fostered by a cognitive and behavioral environment that encourages divergent thinking and exploration of new ideas.
Psychological Safety
Psychological safety is the belief that one can take interpersonal risks without fear of negative consequences. It is crucial for fostering creativity, as it allows individuals to express their ideas freely and take risks without fear of criticism.
Collaborative Relationships
Collaborative relationships involve the exchange of ideas and abilities among team members to achieve a common goal. These relationships are essential for enhancing productivity and fostering a sense of purpose within the organization.
Social Information Processing Theory
The Social Information Processing (SIP) theory explains how cognitive and behavioral responses are shaped by social interactions with leaders and peers. It highlights the importance of a psychologically safe environment for fostering creative behaviors.
Hypothesis Development
Several studies have explored the link between participative leadership and follower radical creativity. The hypotheses tested in this study include the positive correlation between PL and FPS, the mediating role of FPS between PL and FRC, and the moderating effect of collaborative relationships on FRC.
Methodology
The study employed a survey questionnaire method to gather data from managers and followers in the manufacturing industries of Bangladesh. The measurement constructs included participatory leadership, psychological safety, collaborative relationships, and follower radical creativity.
Results
The findings indicate that participative leadership has a significant impact on follower radical creativity, mediated by psychological safety. However, collaborative relationships did not significantly moderate the relationship between FPS and FRC.
Discussion
The study contributes to the existing literature by providing empirical evidence on the role of participative leadership in fostering a creative and psychologically safe environment. It also highlights the complex interplay between collaboration and creativity.
Conclusion
The study underscores the importance of participative leadership in enhancing follower radical creativity in the manufacturing industry. Managers should prioritize creating a psychologically safe environment and fostering collaborative relationships to drive innovation and creativity.
Theoretical Contributions
The study advances the understanding of the dynamics between participative leadership, psychological safety, and radical creativity. It highlights the significance of a safe and valued working environment for creative potential.
Managerial Implications
Managers should engage in inclusive leadership, promote team engagement, and create a psychologically safe climate. Leadership development programs should focus on creating inclusion and psychological safety.
Limitations and Future Directions
The study's cross-sectional design limits causal inferences. Future research should consider longitudinal data, compare different leadership styles, and explore the impact of market factors and environmental uncertainty on the relationship between PL and FRC.